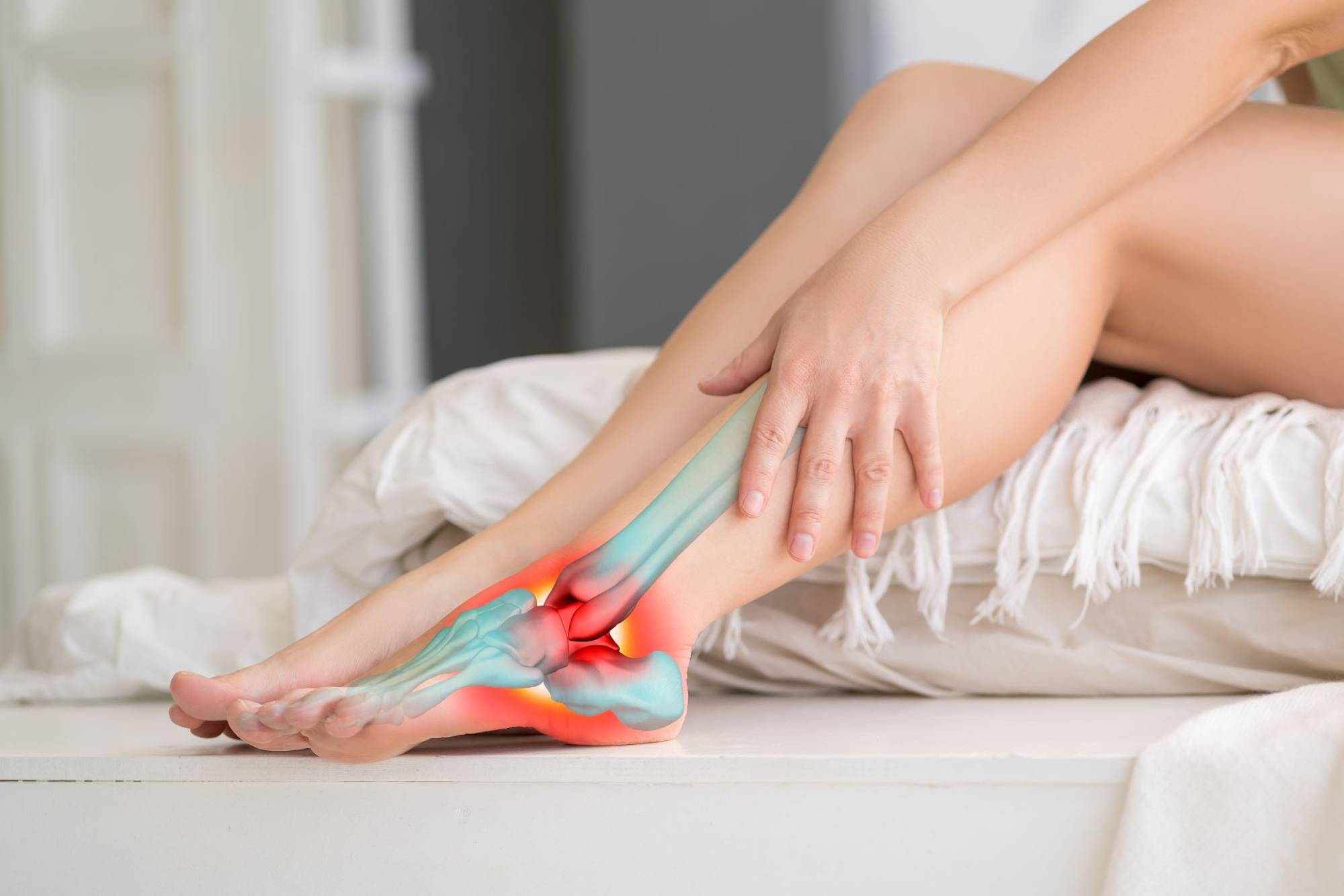
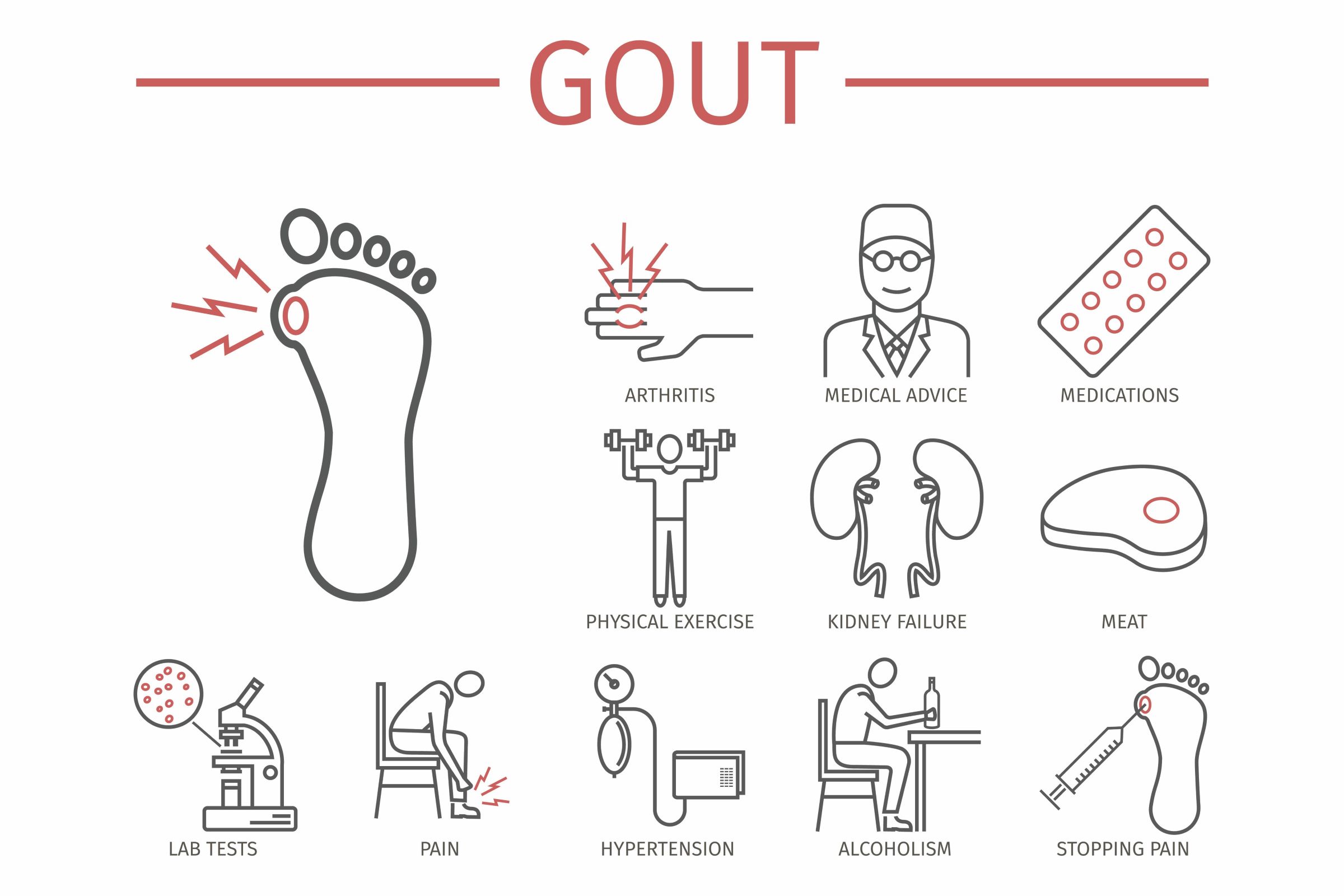
Gout is a chronic and painful type of arthritis that affects many people around the world. It is a form of inflammatory arthritis that is caused by excess uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is made naturally by the body and found in certain foods.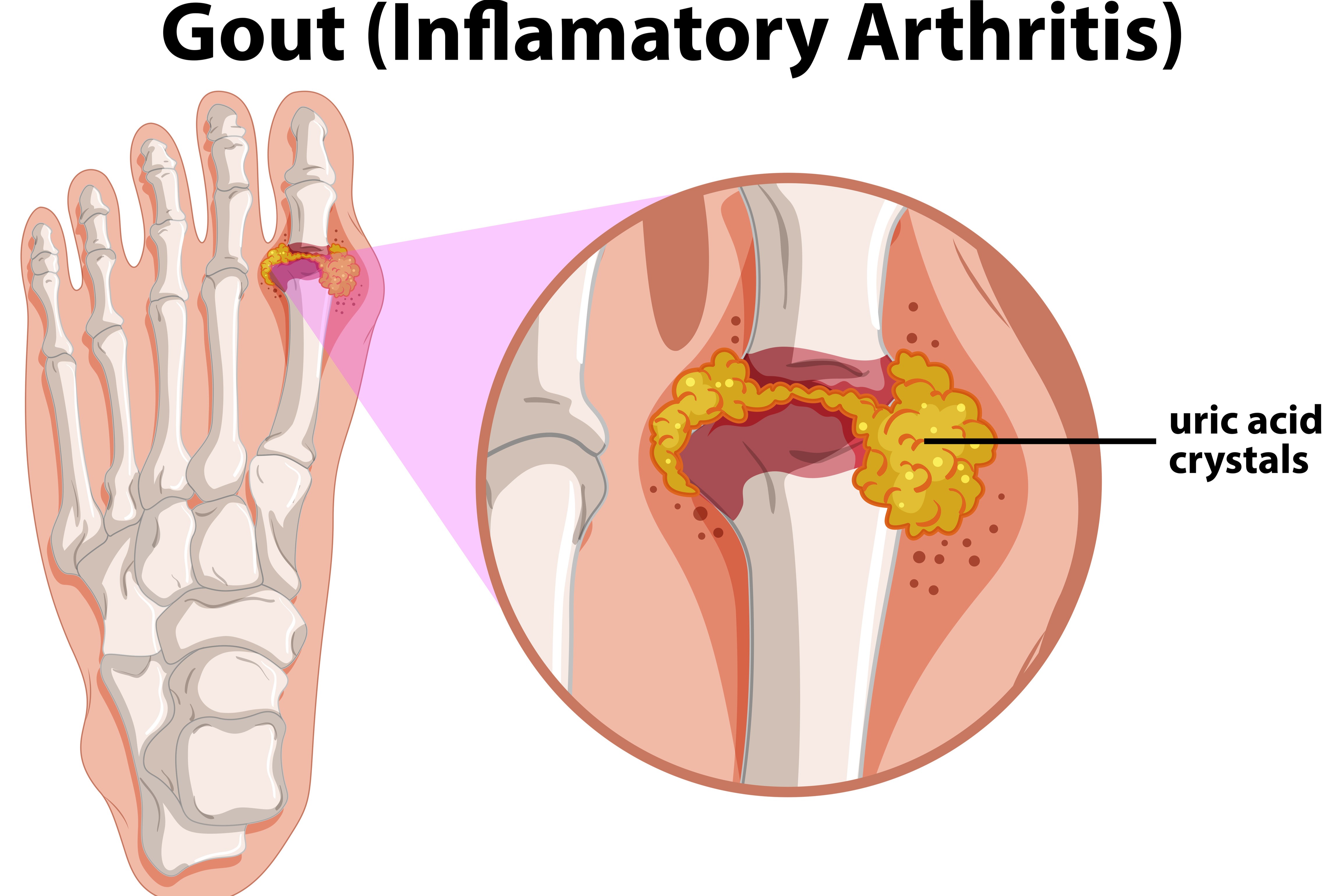
Symptoms
When uric acid levels become too high or the body is not able to efficiently remove it, the excess uric acid forms crystals. These sharp crystals initiate inflammation reaction in the joints that is painful and known as a gout attack. This sudden joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth in the affected joint can last for several days to weeks. The most affected joints are the big toe and the knee. While gout is a chronic condition, there are periods of remission in between attacks where a person is symptom-free.
Diagnosis
To diagnose gout, a doctor will take a series of tests and examinations. A thorough medical history of the symptoms, medications, and family history will be reviewed along with a physical exam to note the appearance of the affected joint. To confirm a gout diagnosis, a joint aspiration or arthrocentesis can be done. A sterile needle is inserted in the affected joint to take out fluid that will be examined under a microscope for urate crystals. Blood tests and x-rays can be done to support a gout diagnosis and rule out another condition but are not required.
Management of Symptoms
Effective management is essential to decrease the occurrence of attacks as there is no cure. Long-term medications such as Allopurinol, can help lower uric acid levels and prevent future attacks. Other medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids can be used during flares to decrease pain and inflammation. Monitoring your diet is key as foods such as red meat, shellfish, beer, and some types of seafood can trigger an attack. Exercising regularly and managing your weight is important as excess weight leads to higher uric acid levels and increases the risk of gout. While there is a genetic predisposition to developing gout, lifestyle modifications such as the ones mentioned can help manage this condition.